Here we outline the expected metrics for successful CUT&Tag sequencing, including number of sequencing reads, duplication rates, and data from CUT&Tag control reactions.
CUT&Tag sequencing metrics
Libraries should be sequenced to a depth of 5-8 million total reads.
For sufficient coverage, each library should generate 3-5 million unique reads after removing multi-mapping reads, duplicate reads, and reads in DAC exclusion list regions).
Deeper sequencing is recommended for rare targets and low inputs.
For experimental targets, genomic enrichment and peak structure should be consistent with biological function.
Read duplicates
High read duplicate rates are common in CUT&Tag due to assay sensitivity and extremely low background.
In general, duplication rates are higher for low abundant PTMs (H3K4me3; 50-70%) compared to abundant PTMs (H3K27me3; 10-30%)
Note that excessive PCR amplification and/or sequencing (>10 million total reads) may increase read duplicates, but good data are still obtained.
If duplicate reads are a problem, see the CUT&Tag Optimization and Troubleshooting section of this site for guidance, starting with this article.
CUT&Tag controls
H3K4me3, H3K27me3, and IgG controls should show expected enrichment and peak structures (Figure 1). Experimental replicates should be highly reproducible.
The SNAP-CUTANA™ K-MetStat Panel should comprise ~1% of unique reads and produce expected results in H3K4me3, H3K27me3, and IgG control reactions.
To understand how control reactions and SNAP-CUTANA Spike-ins can be used to determine assay success, see this article.
Looking help with sequencing analysis?
For help with CUT&Tag sequencing analysis, including genomic alignment, peak calling, and signal-to-noise calculations, see this article.
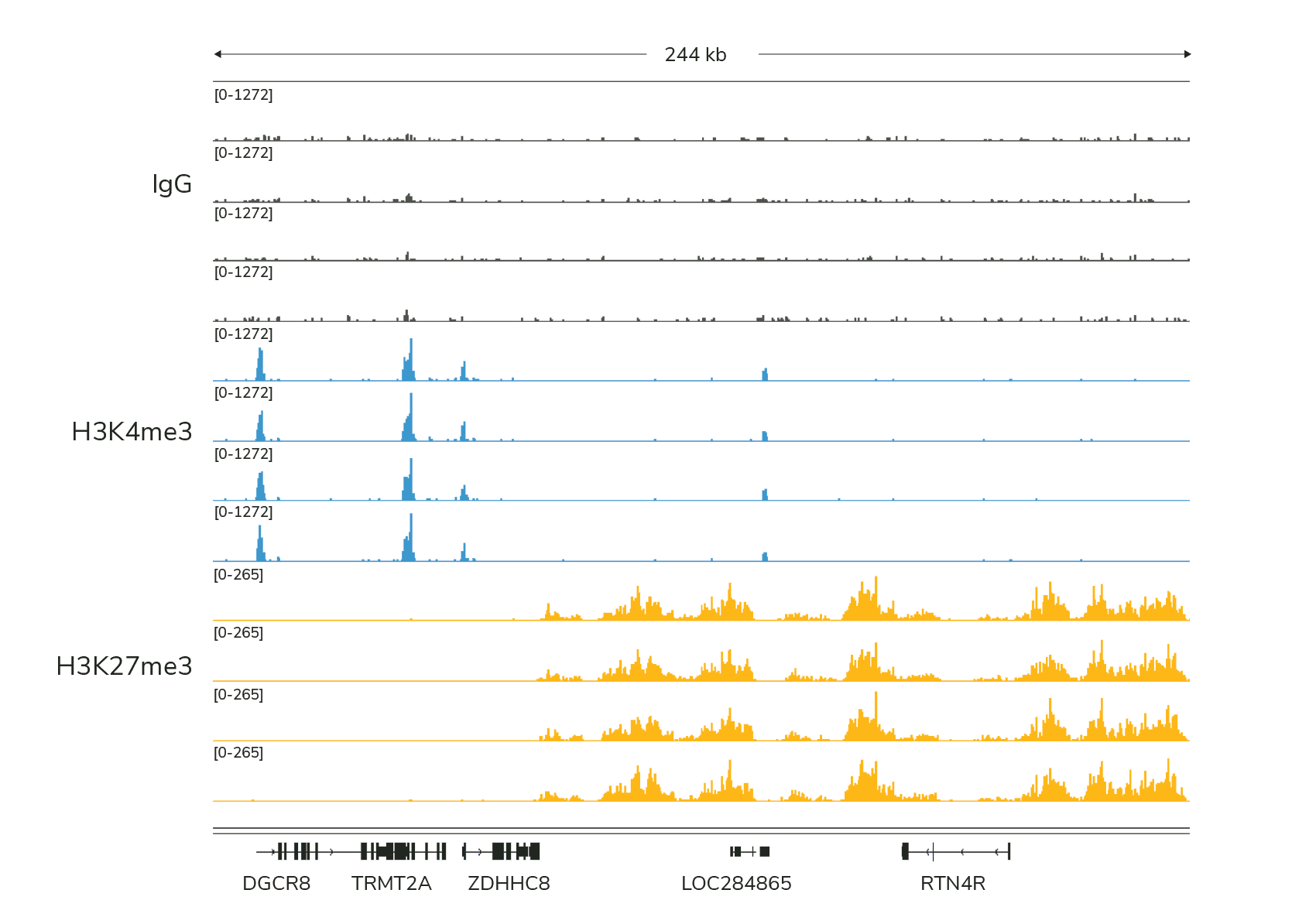
Figure 1. Data across four technical replicates in a CUT&Tag experiment demonstrate the reproducibility of the H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 positive controls and IgG negative control included with the CUTANA™ CUT&Tag Kit. H3K4me3 tracks show sharp peaks localized to transcription start sites (TSSs), while H3K27me3 tracks show broad peaks over repressed regions. IgG shows typical low background. Data were generated using 100,000 K562 nuclei were used per reaction and 5-8 million total sequencing reads per library.