Fiber-seq involves three main steps:
Step 1: Hia5 labeling
Isolated nuclei are incubated with the Hia5 enzyme for ~10 minutes.
Hia5 introduces 6mA marks at accessible DNA sites, enabling open chromatin mapping.
Step 2: Long-read sequencing
Libraries are prepared for PacBio HiFi or ONT platforms (PCR-free workflows only).
Sequencing detects both Hia5-labeled 6mA and endogenous 5mC sites.
Step 3: Data analysis
Data is analyzed using the fibertools pipeline to infer nucleosome positioning, transcription factor binding, and chromatin accessibility. For more on data analysis, see this article.
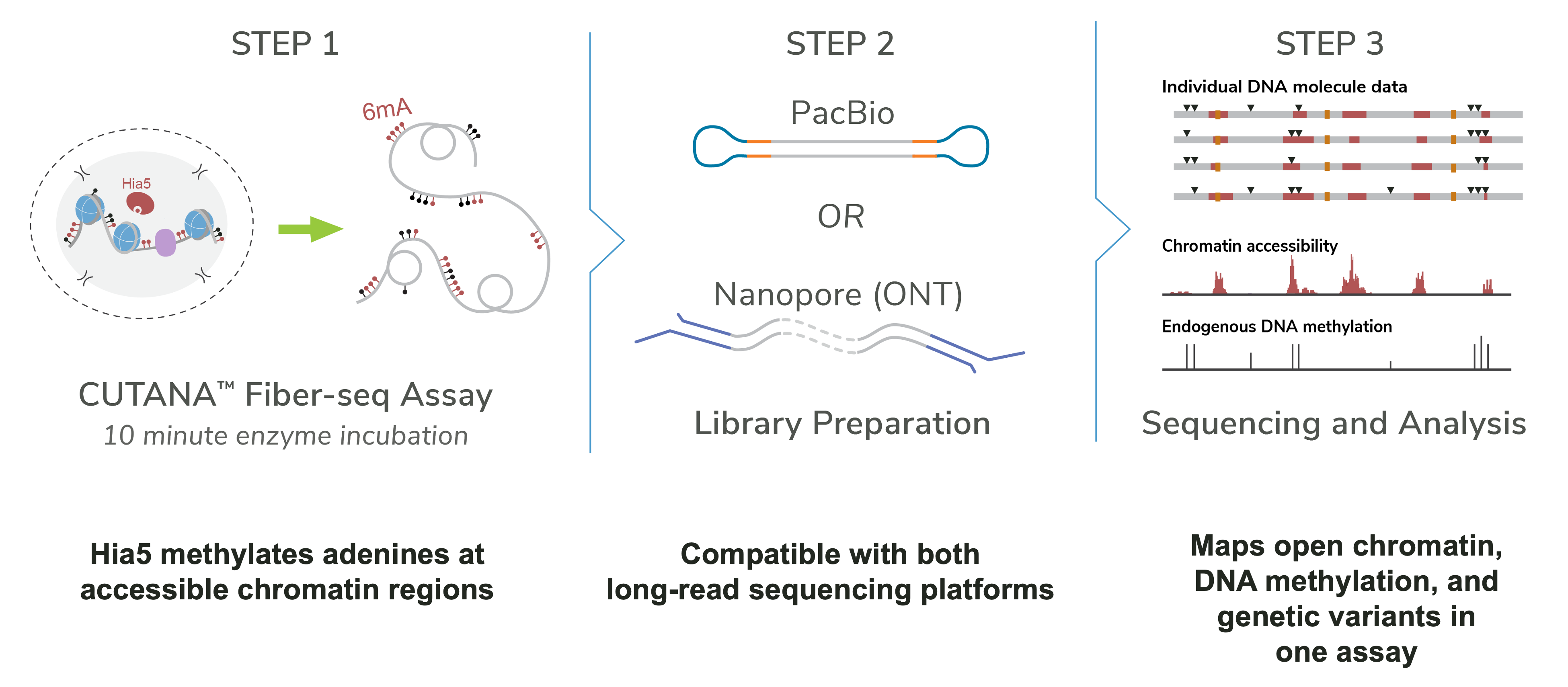
Figure 1: Schematic of the CUTANA™ Fiber-seq workflow. Step 1: Hia5 methyltransferase labels accessible chromatin regions by methylating adenines (6mA) during a 10-minute enzyme incubation. Step 2: DNA is prepared for long-read sequencing using either PacBio or Nanopore (ONT) platforms. Step 3: Sequencing and analysis provide single-molecule resolution maps of chromatin accessibility, endogenous DNA methylation, and genetic variants in a single assay.